What is HACCP?
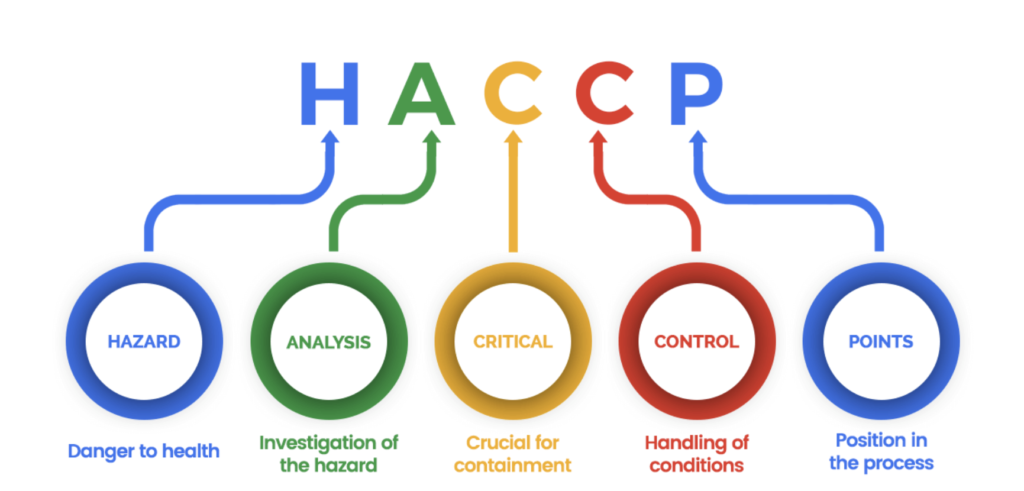
HACCP stands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points. HACCP is a Food Safety Management System that strives to proactively identify food safety risks and devise strategies to decrease or eliminate them from the point of food production to the point of consumption.
Compliance with HACCP is also a legal requirement in some countries. Therefore, HACCP compliance depends on the regulations in your area and the type of food business you are in. For example, the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) require mandatory HACCP certifications for juice and meat.
What is HACCP System?
HACCP addresses food safety by ensuring processes are in place to analyse and control physical, biological and chemical hazards starting from raw material production and procurement till the finished product reaches the plate of a consumer.
At present, HACCP is considered the best system available to prevent food-borne illnesses and is used extensively by the food industry, including food services. HACCP was developed by the Pillsbury Company in the late early 1960s to ensure safe food provision for America’s space program. The goal of this standard is to avoid hazards rather than inspecting finished products for the effects of those hazards.
Why is HACCP Important?
The purpose of HACCP implementation is to reduce the risk of unsafe food which is purely based on science. Having a HACCP certification increases the confidence of the stakeholders in the final product produced by the company as they are assured of the safety of the food. By implementing HACCP, your organization can:
- Prioritize and manage potential food safety issues.
- Control major food hazards, such as microbiological, chemical, and physical pollutants.
- Provide confidence to stakeholders that food was produced safely.
- Cover all forms of potential food safety risks, whether they occur naturally in the food, or caused by the environment, or caused by a production error.
- Help you comply with legal requirements.
Why is HACCP Certification Required?
HACCP certification demonstrates your commitment to food safety and increases confidence in your products or services. This, in turn, helps you compete better in the world market, brings in more business opportunities and increases your profits.
Also, while facing regulatory or other audits, this evidence-based approach can be especially useful.
By following HACCP in your organization, you can utilize the resources more effectively, give a timely response to food safety problems and in the long run, gain financial benefits. HACCP approach is proactive which allows you to identify issues with food safety that could occur anywhere in the supply chain and then develop a strategy to prevent them from happening.
The Steps for Developing a HACCP Plan
There are seven important steps or principles that need to be followed in HACCP:
- Conducting a hazard analysis – The hazard analysis is the first and foremost step in the HACCP process. The relative risk of each hazard must be assessed, and measures must be devised to prevent, eliminate, or control the hazards.
- Making a list of Critical Control Points (CCPs) – Using the commodity flow diagram, the HACCP team determines if there is a chance of a potential hazard at this step. They also determine if any control measures is present at this point for the hazard. In case adequate control measure is not available, and there is no other control measure at another step for the hazard, and is critical to ensure food safety, the particular step in the flow diagram is defined as a Critical Control Point for the particular hazard. Control measures can be adopted and hazards can be minimised, removed, or lowered to acceptable levels at critical control points in the process.
- Setting up of important boundaries – The control points’ critical limits will be established next. The maximum or minimum limit that must be met is specified. These are found in scientific research or regulatory norms. Temperatures, pH levels, and visual appearances are frequently used as criteria for setting those limits.
- Monitoring critical control points – The efficiency of the HACCP strategy depends on how well it is monitored. Each crucial control point must have its own set of restrictions. It’s critical that the procedures enable swift corrective action to be taken.
- Determining corrective actions – Corrective actions must be taken when a deviation occurs at a critical control point. To prevent, remove, or minimise dangers to a tolerable level, predefined procedures are used. It is critical to act quickly to prevent the release of potentially harmful food.
- Establishing methods for verification – It is very important to evaluate and verify if all of the processes established steps are following the plan on a regular basis. This could entail a review of the data, machine maintenance, or ensuring that measures are working as intended. To keep the food and consumers safe, HACCP procedures must be successful.
- Establishing procedures for keeping records – The last step is to keep meticulous records of the plan and practices. It demonstrates that the appropriate procedures have been followed and the food has been handled safely.
Key Activities Required to Address HACCP Principles
The development of a HACCP food safety plan is a critical step in maintaining food safety in the food sector. Some of the key activities involved in creating a HACCP plan are:
- Forming an interdisciplinary team
- Laying out product and market data
- Drawing a commodities flow diagram and getting onsite confirmation of the flow diagram
- Identify and analyse hazards (which the principle 1 of the 7 principles elaborated below).
- Determine Critical Control Points (Principle 2)
- Establish critical limits for each CCP (Principle 3)
- Establish a monitoring procedure (Principle 4)
- Establish corrective action (Principle 5)
- Verify the HACCP plan (Principle 6)
- Keep records (Principle 7)
How to Get HACCP Certification?
The following are the steps that should be followed to obtain the HACCP certification:
1. Understand the Requirements of HACCP
Before a certification program is started in the organization, it is important that employees know the requirements of HACCP. HACCP mentors who are trained by International HACCP Alliance can take this course or you can hire an external consultant if you do not have this expertise in-house.
2. Develop a HACCP Plan
The next step is to develop a HACCP plan for the products and services that your organization provides. The HACCP plan should also cover any regulatory requirements that you need to comply with. Also identify the scope in this phase which is typically comprised of the areas, products/services, processes, or locations that will undergo audits.
3. Conduct a Gap Analysis
You can get a HACCP gap analysis done to map it with the requirement of the standard. This will help you identify actions that you need to take to meet the requirements of the standard.
4. Select a Third-Party Certification Body
The next step is to get food audits done by third-party auditors. While hiring a third-party agency for audits, ensure that they have the required accreditation and qualifications to conduct such audits.
5. Undergo HACCP Audits
HACCP audits are conducted in two stages. You will be requested to provide essential documents for the first stage of the audit. Typically, the auditor will assess the company’s readiness by comparing the documentation provided with the actual standards in the food safety management system. An auditor will identify any gaps in documentation against the standard and request corrections. After successful completion of this stage, the auditing process progresses to the second level, which is more in-depth. The Management system implementation will be evaluated at this point by the auditors. They will conduct onsite audits, interview relevant employees, and look into the evidence and HACCP plan. After a successful Stage 2 audit, your organization will be provided with a HACCP certificate.
Who Provides HACCP Certification?
HACCP Certification is done through a third-party Auditors. Choosing a third-party auditing body, which might be a volunteer certification body for food auditors under the Accredited Third-Party Certification program, is an important step in the auditing process. The auditor should have the proper qualifications and should be licensed to perform the audit before being hired. This ensures that the auditor chosen is qualified to assess the manufacturing process.
Author: Jacqueline Russell

Jacqueline Russell
Jacqueline has an extensive background in Food Science with many years of experience in Quality, Health and Safety Management from multiple industries including; manufacturing (food and packaging), health and fitness and the construction industry.
 100% success – Certification is guaranteed!
100% success – Certification is guaranteed!

Improved operational control

We are ISO 9001 certified

User friendly systems trusted by certification bodies and auditors.

Get a system within 6-8 weeks
What our Clients Say
“ISO Global proved that the process doesn’t have to be difficult, lengthy or stressful”
“Our certification auditor described the system as “excellently done”
“Thank you and your team for the hard work and for holding our hand along the way”
